The GEQ index is divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant comprises of certain selected indicators, which are scored, aggregated and ranked. This section presents the methodology and provides information about each indicator included in the index. It also lays down any assumptions taken for missing data points and methodology used to fill the necessary gaps.
Scoring methodology
Scoring is calculated by using “min – max” formula
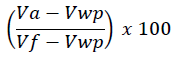
Where “V” is the raw value, “a” is country for which the score is being calculated, “wp” is the value of the worst performer and “f” is the value of the best performing country.
This will result in a standardised score for each country ranging from 0 to 100, 100 being the ideal state. For some indicators, where there is already a calculated index or score computed by a reputed organisation, the index or the score is taken as is. If the score is not based on a standardised scoring of 0 to 100 then the above formula is applied to derive the same.
Indicator Weightage and definition
-
Population growth ... 50%
-
Population growth is the annual population growth based on the de facto definition of population which counts all resident regardless of legal status or citizenship. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Countries who has growth rate between (0.5) and +0.5 percent are given highest possible score of 100. Outside this range, scores decrease linearly as the distance between the optimal value and the actual value increases. Source: (The World Bank, 2019c)
-
Population density ... 50%
-
Population density midyear population divided by land area in square kilometres (population based on national censuses estimates). Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Upper limit value has been fixed to 250. Any country with more than this threshold is given a zero score. Countries with lower population density are given higher scores. Source: (The World Bank, 2019c).
-
Aging Population growth ... 50%
-
Aging Population growth is the annual population growth based on the de facto definition of population which counts all resident regardless of legal status or citizenship. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Best score is given to the countries where the aging population growth lower. Source: (The World Bank, 2019c).
-
Working population ... 50%
-
Working population is the population between the ages 15 to 64 as a percentage of the total population. It reflects the dependency per person of a country. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Best score is given to the countries where the working population is higher. Source: (The World Bank, 2019c).
-
Carbon emission per capita ... 50%
-
Carbon dioxide emissions are those stemming from the burning of fossil fuels and the manufacture of cement. They include carbon dioxide produced during consumption of solid, liquid and gas fuels and gas flaring. Carbon dioxide makes up the largest share of the greenhouse gases contributing to the global warming and climate change. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Countries with the lower CO2 emission per capita are given higher scores. Source: (The World Bank, 2019b).
-
PM2.5 air pollution ... 50%
-
PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter) is defined as the average level of exposure of a nation's population to concentrations of suspended particles measuring less than 2.5 microns in aerodynamic diameter, which are capable of penetrating deep into the respiratory tract and causing severe health damage. Exposure is calculated by weighting mean annual concentrations of PM2.5 by population in both urban and rural areas. Air pollution affect the health of the world’s people. It also carries huge economic costs and represents a drag on development, particularly for low- and middle-income countries and vulnerable segments of the population such as children and the elderly. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Countries with the lower PN2.5 air pollution per cubic meter are given higher scores. Source: (The World Bank, 2019b).
-
FDI Outflows ... 50%
-
FDI Outflow can increase the investment competitiveness crucial for long-term sustainable growth. It is used by some countries as a catchup strategy to acquire knowledge and technology, upgrade production processes, boost competitiveness, augment management skills and access distribution networks (Stephenson and Perea, 2018). To determine the relative size of the investment, it is looked as a proportion of the country’s GDP. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Countries with the higher proportion of FDI outflow as a % of their GDP are given higher scores. Source: (The World Bank, 2019b).
-
FDI Inflows ... 50%
-
FDI Inflows helps countries to boost their economic growth, human capital enhancement, employment and access to the knowledge and technology. To determine the relative size of the investment, it is looked as a proportion of the country’s GDP. Scoring is calculated by min – max formula; Countries with the higher proportion of FDI outflow as a % of their GDP are given higher scores. Source: (The World Bank, 2019b).
